 |
||
|
|
||
|
Page Title:
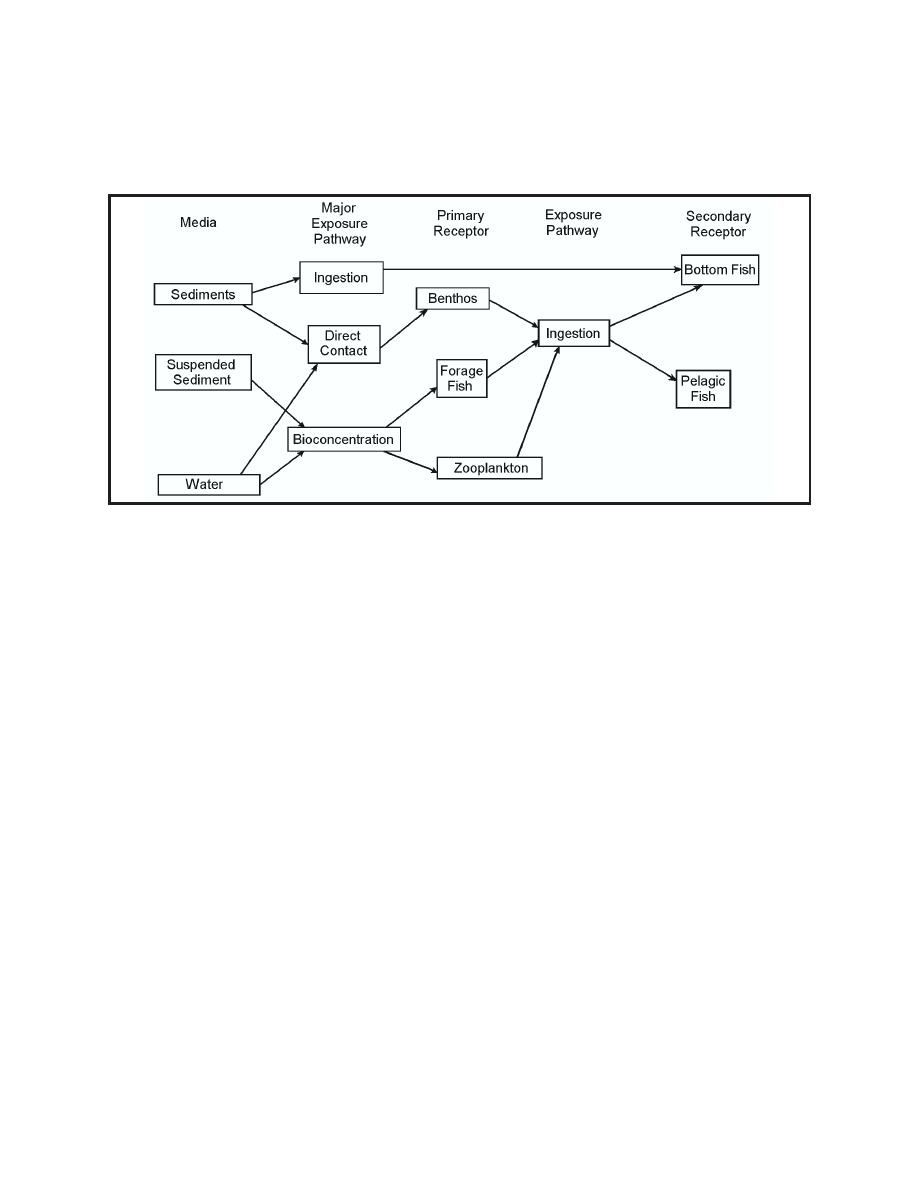
Figure 6. Risk assessment pathways |
||
| |||||||||||||||
|
|
 ERDC TN-DOER-R2
December 2001
implemented under the ADDAMS toolkit. The user may elect to modify these templates to meet
site-specific needs. Potential changes to the templates could include changes in pathways (uptake
routes), source concentrations, and receptors (Figure 6).
Figure 6. Risk assessment pathways
The scenarios represent generic conceptual models. In this manner, they include the typical sources,
processes, and receptors addressed under no-action and dredging scenarios. The tools utilized for
the scenarios allow the user to estimate exposure concentrations, uptake, and effects for the major
pathways and receptors. However, the user can select other tools and receptors to address
site-specific needs. Both human and ecological risk end points have been included in the scenarios.
The generic scenarios for no-action and dredging impacts are provided as read-only files. Users of
the system will be required to save their site-specific application under a unique file name. This
feature aids the user by not having to create a new starting scenario for each project.
No-action Scenario. The no-action scenario is essential for any dredging evaluation. It allows
the user to estimate net change in risk due to any operation. The no-action evaluation gives the user
an indication of the existing, predredging impact of the sediment deposits and the potential risk of
the no-action alternative. The no-action scenario is useful in developing comparative risk of
multiple alternatives.
The conceptual model for the no-action scenario is shown in Figure 7a. The sources of the
contaminants are the sediment and the water column. Interactions between the sources (shown in
Figure 7b) include precipitation, dissolution, resuspension, sedimentation, diffusion, adsorption,
volatilization, decay, and burial as shown in Figure 4. Potential pathways from the sources to the
receptors include ingestion of the sediments or water, direct contact with sediment or water,
bioconcentration from the water column, and bio-uptake of organisms. The receptors are humans,
piscivorous birds, pelagic fish, forage fish, bottom fish, benthos, and zooplankton.
8
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us - Support Integrated Publishing |