 |
||
|
|
||
|
Page Title:
Table 1. Standard Geotechnical Laboratory Test Procedures |
||
| |||||||||||||||
|
|
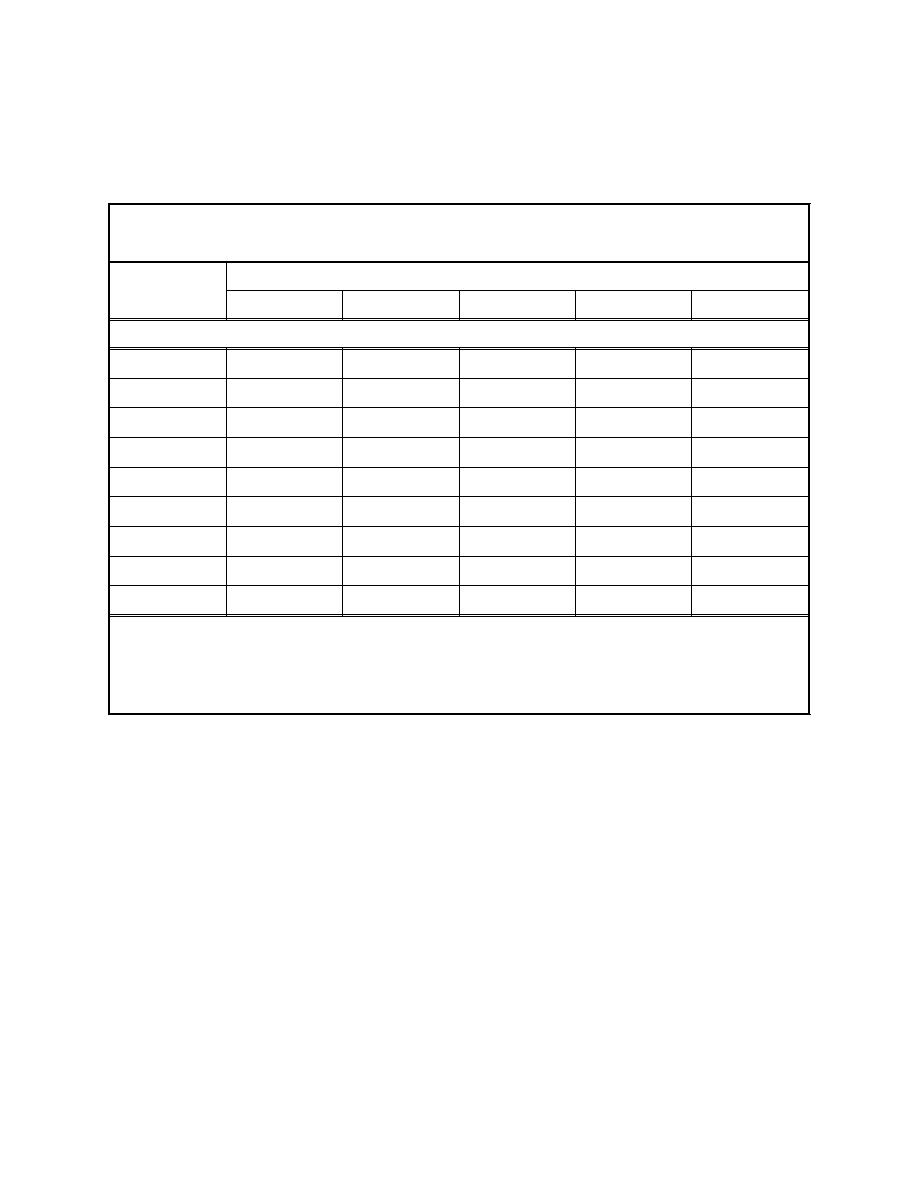 Transportation Officials (AASHTO), or the USACE, should be used for
each test. Table 1 gives the standard ASTM and USACE designations for
the needed tests and also cross-references these procedures to those of sev-
eral other organizations that have standardized test methods.
Table 1
Standard Geotechnical Laboratory Test Procedures
Designation
COE1
DoD2,3
Test
ASTM
AASHTO
Comments
Soils
Water content
D 2216
T265
I
Method 105, 2-VII
Grain size
D 422
T88
V
2-III, 2-V, 2-VI
Atterberg limits
D 4318
T89 T90
III
Method 103, 2-VIII
Classification
D 2487
III
Specific gravity
D 854
T100
IV
2-IV
Organic content
D 2974
Use Method C
Consolidation4
D 2435
T216
VIII
Permeability5
D 2434
T215
VII
Shear tests
D 2573
Field test
1
Department of the Army Laboratory Soils Manual EM 1110-2-1906.
2
Department of Defense Military Standard MIL-STD-621A (Method 100, etc.).
3
Department of the Army Materials Testing Field Manual FM 5-530 (2-III, etc.).
4
Do not use the standard laboratory test for determining consolidation. Instead, use the modified standard consolidation
test and the self-weight consolidation test as described in USACE (1987).
5
One value of permeability must be calculated from the self-weight consolidation test.
Additional geotechnical data should also be collected on contaminated
sediments for capping projects, including consolidation, and shear
strength data. These data are useful for geotechnical evaluations of stabil-
ity of the capped deposit and the development of mound or deposit geome-
tries. Detailed information on consolidation testing is presented in
Appendix I.
Physical analysis of dredging site and/or disposal site water may also
be required to include suspended solids concentration and salinity. Poten-
tial stratification due to temperature and salinity differences should be
considered. These data must be developed using standard techniques.
Chemical/biological characterization
Capping as a control measure is normally considered only after a
sediment to be dredged is found to be contaminated. In order to make
such a determination, some chemical and biological characterization of
17
Chapter 3 Characterization of Contaminated and Capping Sediments
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us - Support Integrated Publishing |