 |
||
|
|
||
|
Page Title:
Table 1. Advantages and Limitations of Risk Assessment |
||
| |||||||||||||||
|
|
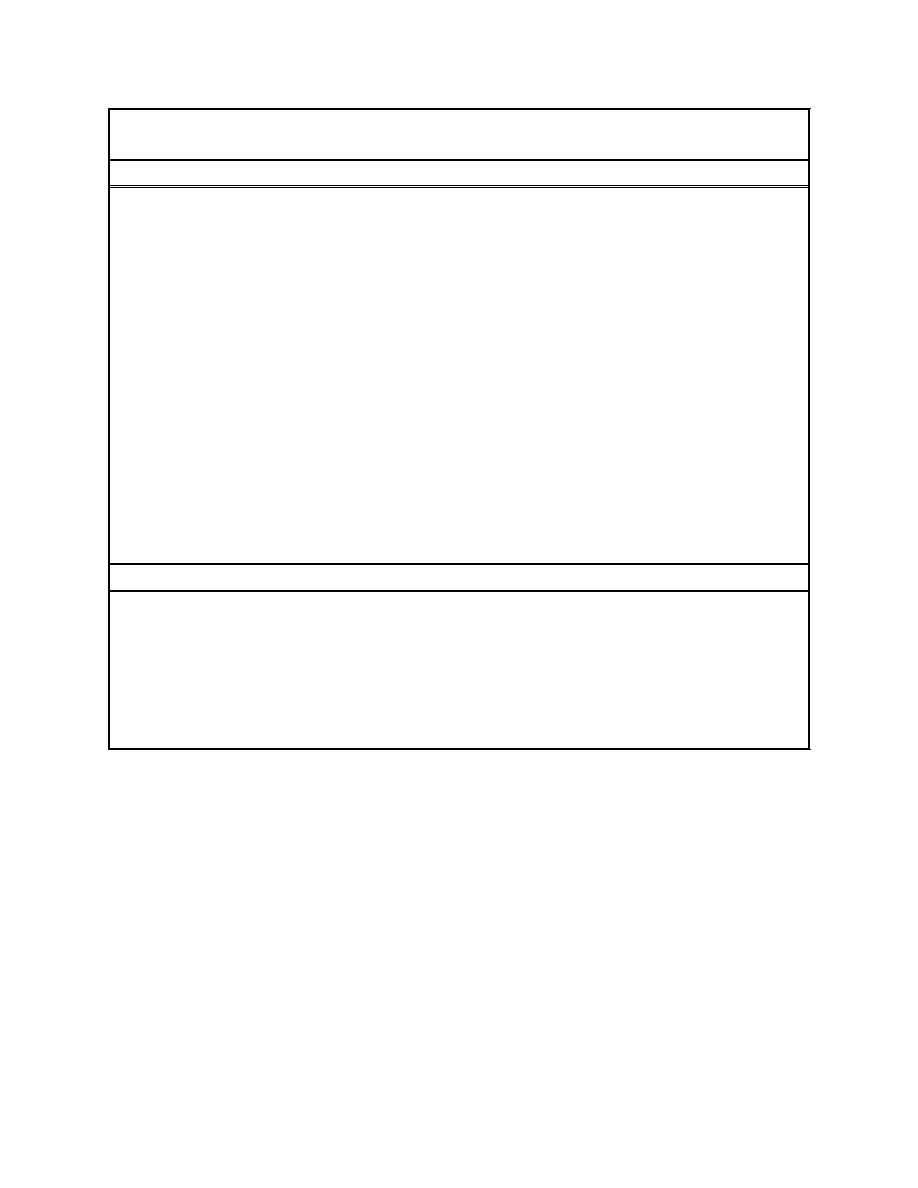 Technical Note DOER-R1
September 1998
Table 1
Advantages and Limitations of Risk Assessment
Advantages
Site and Technology Specific
Can address site- and technology-specific contingencies and variations without being overly
conservative (avoids the pitfalls of numerical standards)
Flexible
Can modify the organism's estimated exposure based on site-specific information
Iterative
Can apply "what if?" scenarios to evaluate the effects of various assumptions or changes in design
for a given disposal alternative
Inclusive
Accommodates the input of various interested parties, often referred to as stakeholders
Objective
Focuses upon several endpoints and presents an estimate of risk with reference to these endpoints
Avoids false positives
Avoids false positives associated with simple statistical comparisons between reference and test
sediments
Transparent
Makes the decision-making process more explicit
Value Added
Use the same risk assessment at a site with multiple projects over several years
Limitations
Results are site specific
Risk assessment results cannot be universally applied in the same manner as a criterion or advisory
level
Dependent on extrapolations
Fate and transport models, toxicity estimates, and exposure estimates will use extrapolations from
various data sets with varying degrees of uncertainty
Requires careful and complete communication of uncertainties
The uncertainty in a risk estimate must be explicitly described for each extrapolation or risk estimate
Even relatively complex risk assessments are easily iterated because the calculations of exposure
and risk are easily automated on computer spreadsheets. This allows the dredged material manager
to apply what-if scenarios to evaluate the effects of various assumptions or changes in a given
disposal alternative. This can be a significant advantage in choosing among alternative management
options or selecting sites. This property of risk assessment is also useful in attempting to decide
how the timing of disposal may affect an outcome by making different assumptions regarding
various seasons (i.e., helping to decide upon appropriate "environmental windows").
Risk assessment is inclusive because it can accommodate the input of various interested parties,
often referred to as stakeholders, in the risk management process. These stakeholders may be
regulators, state agencies, commercial interests, or environmental groups. Where appropriate or
necessary, the risk assessment considers their input in the development of exposure scenarios. The
exposure scenarios are the particular, site-specific, and detailed descriptions of how a human or an
5
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us - Support Integrated Publishing |