 |
||
|
|
||
|
Page Title:
Considerations for Capping Material Placement |
||
| |||||||||||||||
|
|
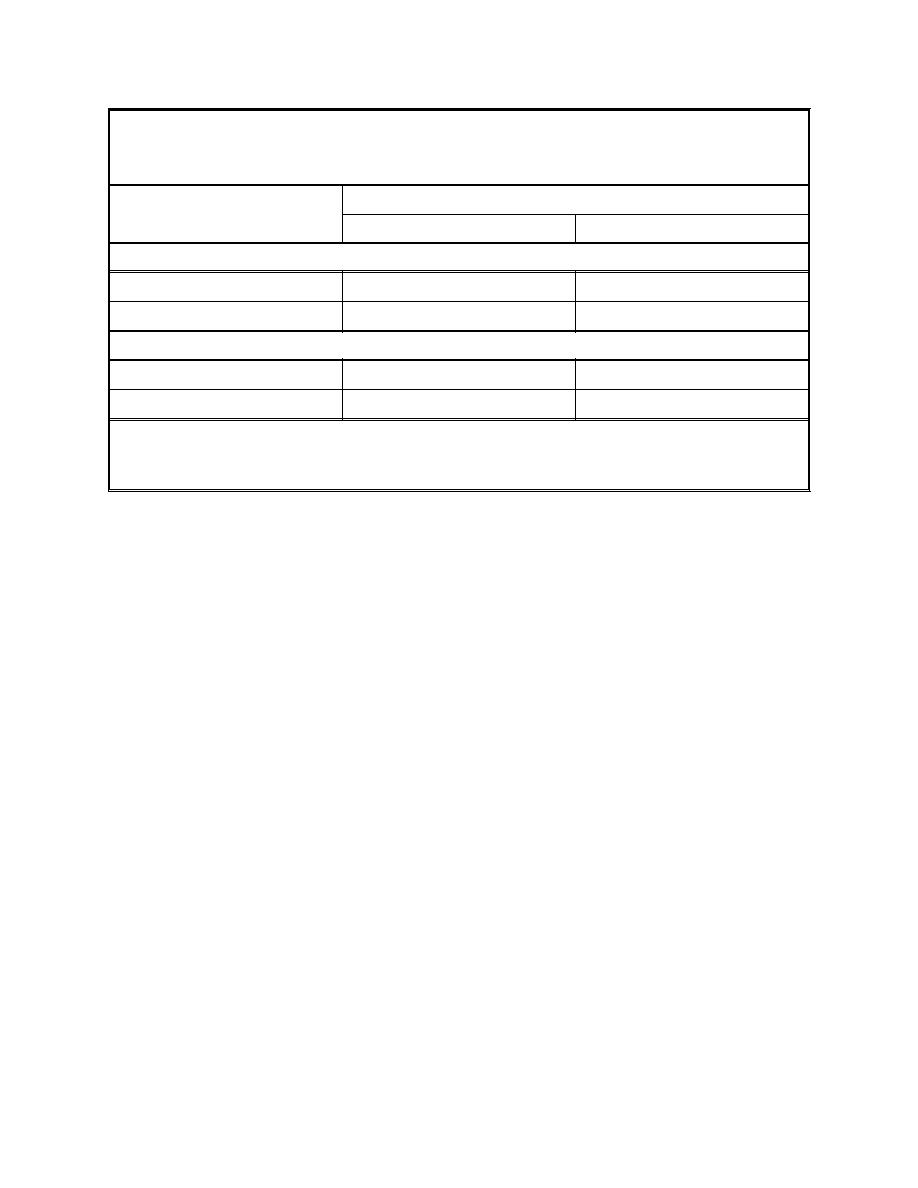 Table 2
Flow Characteristics of Dredged Material Placed in Aquatic Sites (Shields and
Montgomery 1994)
Placement Method
Dredged Material Characteristics
Point Dump
Pump Down
Nocohesive Material
Mechanically Dredged
Tends to mound
Not applicable
Tends to flow1,2,3
Tends to mound4
Hydaulically Dredged
Cohesive Material
Tends to mound1,2
Mechanically Dredged
Not applicable
Tends to flow1
Tends to flow2
Hydraulically Dredged
1
JBF Scientific Corporation 1975.
2
Morton 1983a.
3
Sustar and Eker 1972.
4
Nichols, Thompson, and Faas 1978.
water column impacts, controls to specifically reduce water column disper-
sion (for example, submerged discharge) may be required.
For LBC, the dredging equipment and placement technique for contami-
nated sediment must result in a tight, compact mound that is easily capped.
Compact mounds generally result when the material is dredged and placed
at or near its in situ density prior to dredging. This is most easily accom-
plished with mechanical dredging techniques and precision-point discharges
from barges.
For CAD projects, the provision for lateral containment in the form of
a bottom depression or other feature defines and limits the extent of bot-
tom spread. For this reason, either mechanical dredging or hydraulic
placement of the contaminated material may be acceptable for CAD. If
the contaminated material is placed hydraulically, a suitable time period
(usually a few weeks) must be allowed for settling and consolidation to oc-
cur prior to placement of the capping material to avoid potential mixing of
the materials unless capped by slow sprinkling of sand.
Considerations for Capping Material Placement
Placement of capping material is accomplished so that the deposit
forms a layer of the required thickness over the contaminated material.
For most projects, the surface area of the contaminated material to be
capped may be several hundred feet or more in diameter. Placement of a
cap of required thickness over such an area may require spreading the ma-
terial to some degree to achieve coverage.
28
Chapter 5 Equipment and Placement Techniques
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us - Support Integrated Publishing |