 |
||
|
|
||
|
Page Title:
Options if Required Volume is Too Large |
||
| |||||||||||||||
|
|
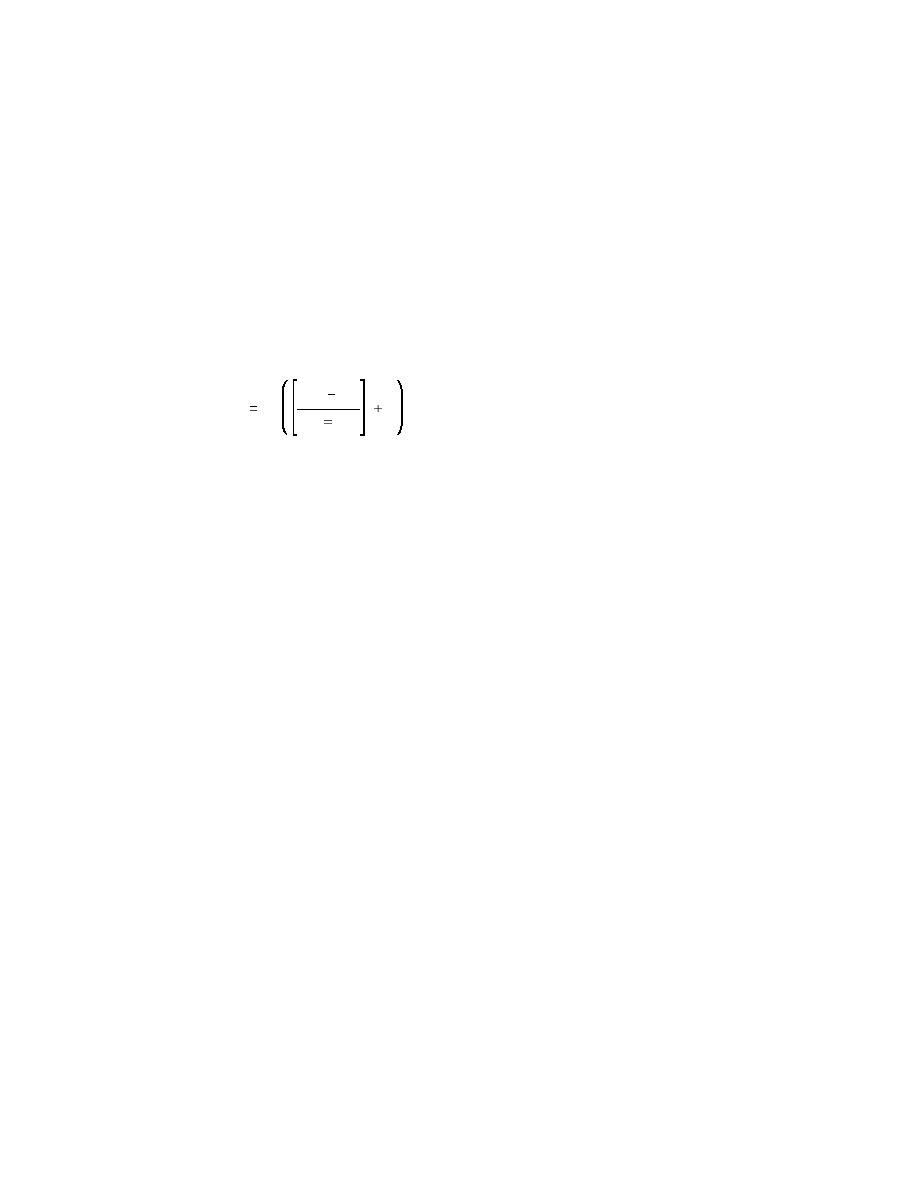 However, the reduction in cap thickness due to consolidation should be
considered from the standpoint of advection of pore water. Consolidation will
reduce the void ratio and thus will force pore water further out into the cap.
Effect on Volume Due to Change in Void Ratio
The volume of material to be dredged for the cap must be calculated to deter-
mine if potential sources of capping material, say from an available maintenance
dredging project, will be adequate. The potential changes in volume due to
dredging and placement must be considered. The required volume of capping
material (in situ in the channel) can be calculated as follows:
ei)
(eo
(H6)
Vc
Vci
1
ei)
(1
where
Vci = volume of cap material in situ in channel
Vc = volume of cap material initially placed
eo = average void ratio of cap material initially placed
ei = average void ratio of cap material in situ in channel
For projects in which the capping material is hydraulically placed, the value
of eo can be determined in the same way as that used in design of confined
disposal facilities (USACE 1987, EM 1110-2-5027). For mechanically dredged
sediments, an approach to determine the minimum cap volume required is to
assume no difference in eo and ei (i.e., Vci = Vc). It is recommended that those
with experience dredging a particular project (USACE District Operations
Division staff, dredging contractors, etc.) be contacted for suggestions on bulk-
ing factors. SAIC (1995) reports that the assumption of no difference in eo and ei
is reasonable.
Options if Required Volume is Too Large
The information from the prior section along with the information in Chap-
ter 6 (main text) on expected contaminated mound footprint should be used to
compute required cap volume. If the estimated cap volume is too large, either
because insufficient cap material is available or the cost is too high, the follow-
ing options are available. As noted earlier, the most obvious is to reduce the
volume of contaminated material. A second option may be to delay dredging
until additional cap material becomes available, perhaps combining several small
H11
Appendix H Level-Bottom Capping Projects
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us - Support Integrated Publishing |