 |
||
|
|
||
|
Page Title:
Table 1. Most Likely Exposure Pathways For Five Dredged Material Management Options |
||
| |||||||||||||||
|
|
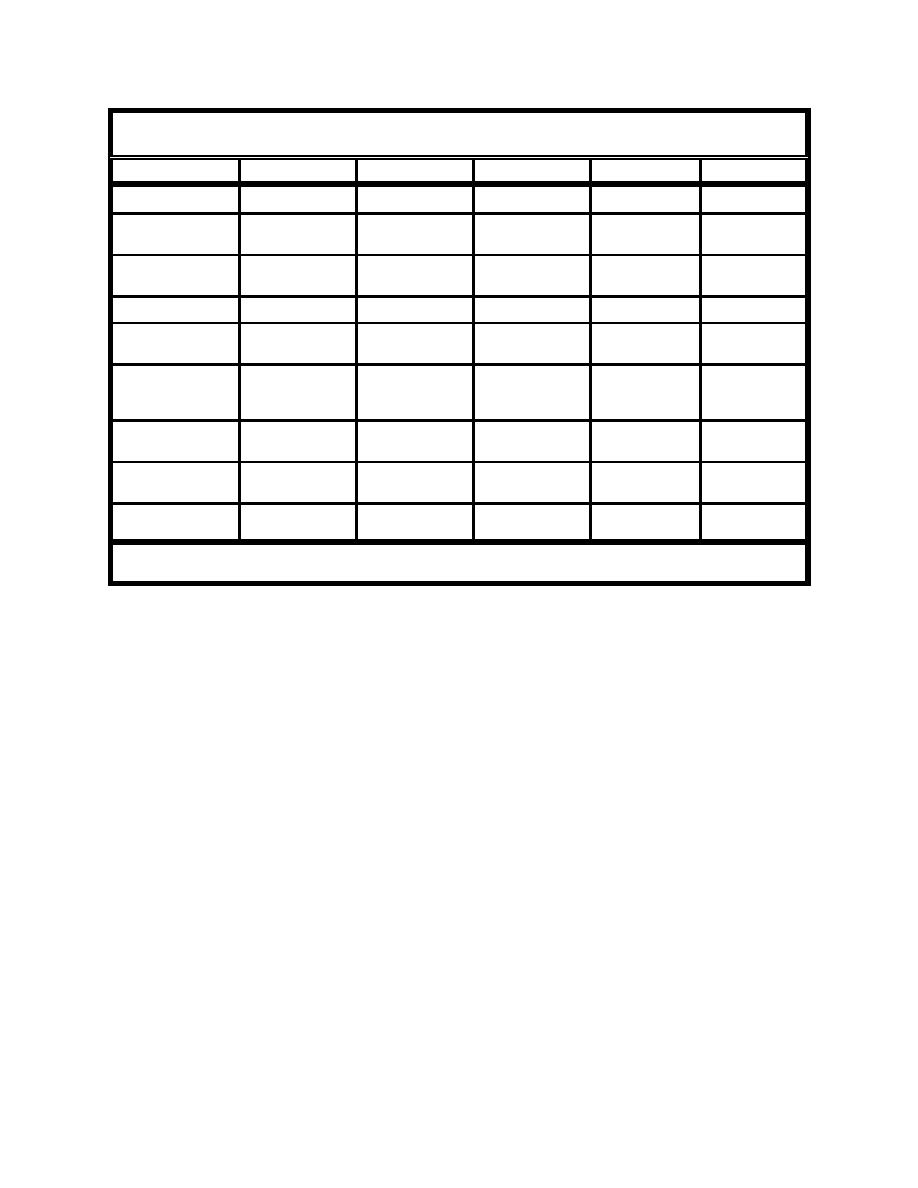 Table 1
Most Likely Exposure Pathways For Five Dredged Material Management Options
Pathway
Unconfined
CAD
Upland
CDF
No Action
Volatilization
L
L
Direct Ingestion
L
L
L
L
(animal)
Resuspension/
L, S
S
S Dewatering
S Dewatering
L
Advection of Particles
Wind Transport
L
Unlikely
L
L
L
L
Advection (transport)
Diffusion
Literature shows
Literature shows
Literature shows
Literature shows
Literature shows
unlikely
unlikely significance
unlikely significance
unlikely
unlikely
significance (a)
significance
significance (a)
Dermal Contact
L
S
L
L
L
(Animal)
Dermal Contact
(Human)
L
L
L
Indirect Ingestion
L
S
L
(human and animal)
L = long-term concern; S = short-term concern; (a) Diffusion may be of some importance from the sediment bed to the water column
under some conditions.
assessments should consider the local, ethnic dietary preferences and methods of
food preparation. Recreational fishing habits may also be very important in
considering diets. For example, some group members have anecdotally observed
numerous recreational fishing boats at dredged material management sites on a
year-round basis.
The group considered the use of caged animal studies to evaluate exposure
pathways. There was a concern that stakeholders occasionally request or require
such studies without a clear sense of how the results will be used in decision-
making. The group felt that caged animal studies should not be considered a
routine measurement method but may be useful in exposure assessment if:
a. There is reason to believe that pelagic exposure pathways are important.
b. They are done in a spatial and temporal series.
c. They are done in conjunction with fate and transport modeling.
5
Chapter 2 Exposure Assessment Workgroup Summary
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us - Support Integrated Publishing |