 |
||
|
|
||
| |||||||||||||||
|
|
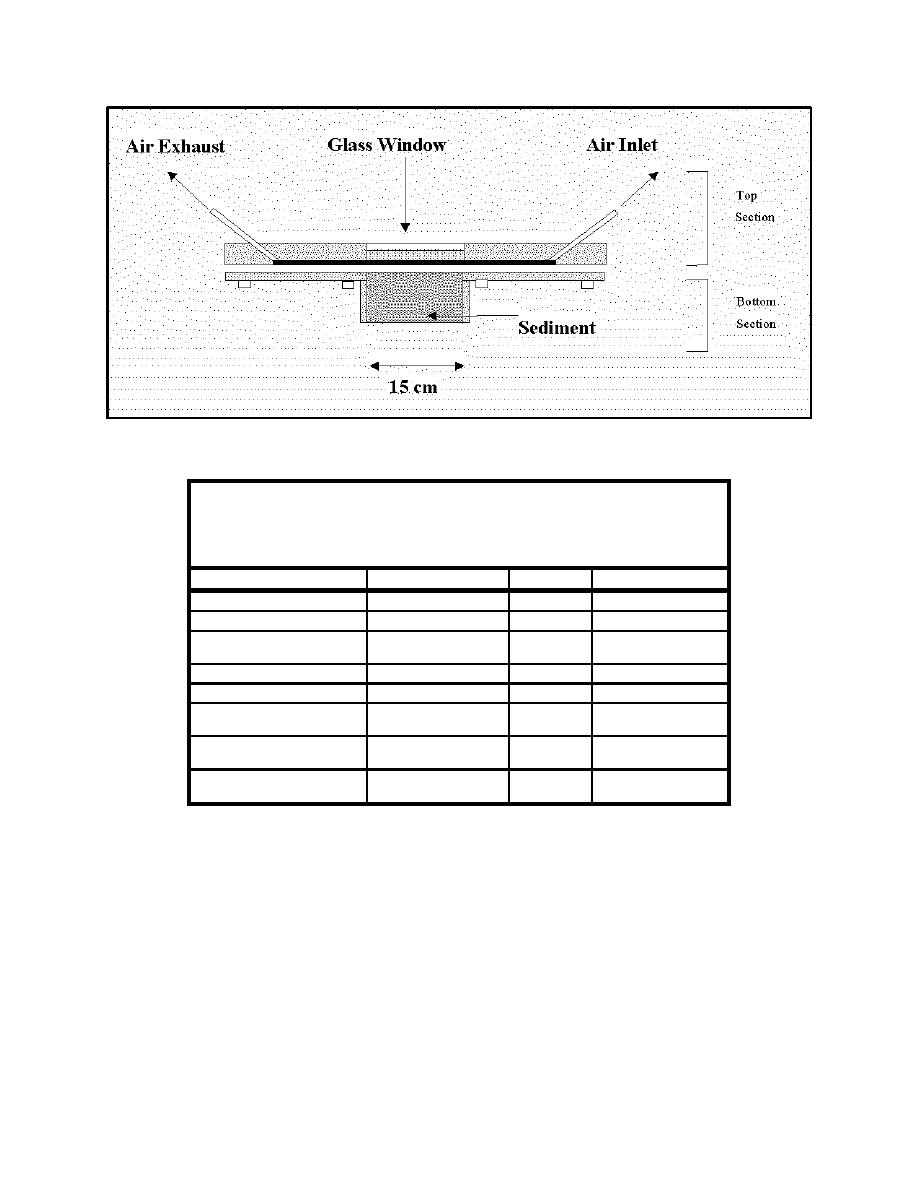 Figure F-1. Flux chamber for quantifying volatile emissions in a laboratory setting
Table F1
Contaminant-Specific Air Sampling Tubes Available through
Supelco, Inc., Bellefonte, PA, and Accompanying Analytical
Method
Contaminant
Trapping Material
Tube Type
Analytical Method
Polychlorinated biphenyls
XAD-2
Orbo-44
EPA Method 8081
Polyaromatic Hydrocarbons
XAD-2
Orbo-44
EPA Method 8270
Total Recoverable Petroleum
XAD-2
Orbo-44
EPA Method 8270
Hydrocarbons
Pesticides
XAD-2
Orbo-44
EPA Method 8081
Ammonia
H2SO4-coated silica gel
Orbo-554
OSHA Method 6015
Treated activated
Hydrogen Sulfide
Orbo-34
NIOSH Method 6013
coconut charcoal
Carbosieve S-111
Dimethyl Sulfides
Orbo-91
NIOSH Method 2542
carbon
Carbosieve S-111
Methyl Mercaptans
Orbo-91
NIOSH Method 2542
carbon
F.2.3 Sediment preparation
Sediment core or grab samples collected from the proposed area of dredging
should completely fill storage containers and be immediately refrigerated (4 EC)
following sampling to preserve sample integrity. Intact core samples, not
removed to a storage container, should be immediately sealed and refrigerated.
To ensure a representative sample, the sediment samples may be composited into
one bulk sample or combined according to horizontal or vertical stratification.
Approximately 20 L of material is needed to perform bulk sediment chemical
and physical characterization and volatile emissions testing. This volume can be
more or less depending upon the number of COC. If COC are trapped on the
same type of material only one chamber is needed to measure emissions, an
F3
Appendix F Laboratory Evaluation of Volatile Emissions and Volatile Dispersion Modeling
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us - Support Integrated Publishing |